How to stimulate a baby’s brain development
Written on 11th December, 2023Stimulating a baby’s brain development is crucial during the early years of life. This period marks a crucial stage of rapid neurological growth and formation of essential neural connections. Through various interactions, activities, and experiences, a baby’s brain begins to build the foundation for future learning, behaviour, and overall health.

Engaging with babies through talking, reading, and interactive play not only encourages language development but also stimulates cognitive skills. These activities help in forming neural pathways that are fundamental for various abilities, including physical development, problem-solving, memory, and attention span.
Additionally, sensory experiences and physical activities contribute significantly to a baby’s development. Exploring different textures, colours, and sounds aids in refining sensory perception, while activities like tummy time support the development of motor skills, coordination, and muscle strength.
Why is it important to stimulate a baby’s brain development?
Brain development
During the first few years, a baby’s brain is rapidly developing, forming connections and laying the foundation for future learning, behaviour, and health. Stimulation during this time promotes the formation of neural pathways that are essential for various skills and abilities.
Learning abilities
Early experiences significantly impact a child’s ability to learn in the future. Stimulation through various sensory play and activities helps in the development of cognitive skills, language, social-emotional skills, motor skills, and more.
Language development
Interacting, talking, and reading to babies stimulates their language skills. It helps in vocabulary development, understanding language patterns, and sets the stage for better communication skills later in life.
Sensory and motor skills
Activities that engage the senses and encourage movement help in refining sensory perception and developing motor skills, which are crucial for coordination and physical abilities.
Social and emotional development
Positive interactions, nurturing relationships, and responsive caregiving contribute to emotional well-being and social skills development in babies. This helps them build trust, empathy, and the ability to form healthy relationships later in life.
Cognitive abilities
Stimulation through play, exploration, and exposure to new experiences supports cognitive development. It encourages curiosity, problem-solving skills, and the ability to think critically.
Resilience and adaptability
A well-stimulated brain tends to be more adaptable and resilient. It helps children cope better with changes and challenges they might encounter later in life.
Long-term impact
The experiences and stimulation a baby receives during the early years lay the foundation for lifelong learning, behavior, and health. Investing in early brain development can have long-lasting positive effects.
Ultimately, providing a stimulating and nurturing environment in the early years of a child’s life supports their overall development and helps them reach their full potential.
What ways can you stimulate a baby’s brain development
Stimulating a baby’s brain development involves creating an environment rich in experiences that encourage exploration, interaction, and sensory engagement.
Talking and Reading
Engage in conversation and narrate daily activities, stories, or songs to your baby. Talking to them helps in language development and builds a foundation for communication skills. Read books together, even if they’re too young to understand the words. It introduces them to language patterns and fosters a love for reading.

Sensory Play
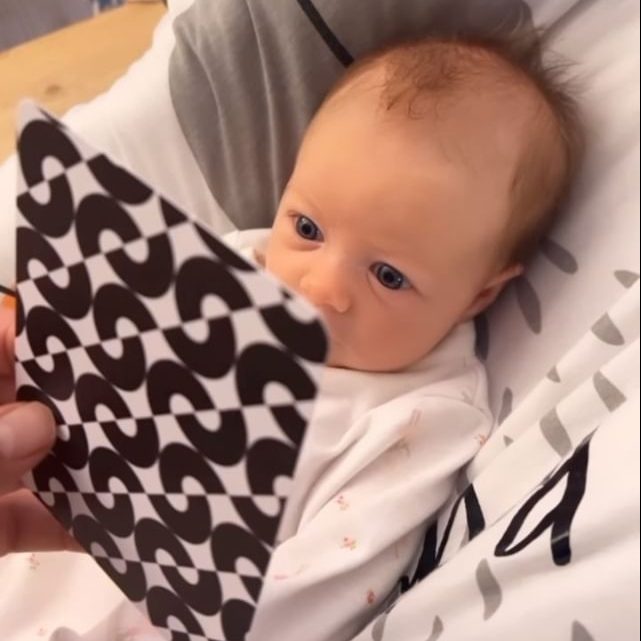
Provide a variety of age-appropriate toys and objects that encourage exploration, such as rattles, textured items, and colourful toys. For younger babies, from newborn to 9 months, Sensory Flashcards for Babies offer one of the best ways to stimulate the initial physical developments – including eye and physical development. Sensory Flashcards are also a great way to use during tummy time. Tummy time helps babies to strengthen their neck, shoulder, and arm muscles and using Sensory Flashcards for Babies can encourage the speed of this development. This also supports the development of motor skills necessary for crawling and later activities.

Music & Sound
Play soft music or sing to them. Musical experiences can have a positive impact on their auditory development and create a soothing atmosphere.
Music plays a significant role in a baby’s development across various domains. It stimulates their senses, especially their auditory faculties, exposing them to different rhythms, melodies, and tones. This exposure aids in sensory development.
Even before they can speak, babies absorb language patterns through music. This exposure helps in language acquisition, fostering their communication skills.
Music has a remarkable ability to regulate emotions. Soft melodies or lullabies create a calming effect, helping babies manage their emotions and fostering a soothing environment.
Experiencing music also supports cognitive development. It helps in memory formation, enhances attention, and aids in recognising patterns, contributing to overall cognitive skills.
When babies respond to music by moving, whether through swaying or tapping their feet, it encourages the development of their motor skills.
Furthermore, engaging in musical activities, such as singing together, fosters social bonding between babies and caregivers. This interaction nurtures emotional connections and supports social development.
Music sparks curiosity and imagination in babies, encouraging creative expression and exploration, which is vital for their overall development.
Lastly, the calming effect of music reduces stress levels for both babies and caregivers, contributing to a relaxed and peaceful atmosphere that supports healthy development.
Tactile Play
Tactile play, involving touch and exploration of different textures, is incredibly beneficial for a baby’s development.
Firstly, it stimulates their sense of touch, which is essential for sensory development. Babies learn about the world around them by touching and feeling various textures, aiding in their understanding of different materials and surfaces.
Tactile play supports the development of fine motor skills. As babies manipulate objects of different shapes, sizes, and textures, they refine their ability to grasp, pinch, and manipulate items with their hands and fingers.
Exploring textures through tactile play helps in cognitive development by fostering curiosity and problem-solving skills. Babies learn cause-and-effect relationships as they discover how different materials respond to their touch.
Engaging in tactile experiences also supports language development. When caregivers describe the textures or sensations babies are experiencing, it introduces new vocabulary and helps babies associate words with tactile experiences.
Moreover, tactile play can have a calming effect on babies. Feeling different textures can be soothing, helping them regulate emotions and providing a sense of comfort and security.
Why is Screen-Free Play important?
Screen-free play is vital for babies’ development for several reasons.
Firstly, it encourages active engagement and exploration of the environment, allowing babies to use their imagination and creativity. Unlike passive screen time, which offers limited interaction, screen-free play involves hands-on experiences that stimulate various senses and foster cognitive, motor, and social development.
Engaging in screen-free play promotes physical activity and motor skill development. Babies have the opportunity to move, crawl, grasp, and manipulate objects, which is essential for their overall physical development and coordination.
Screen-free play also encourages social interaction and bonding. When babies play with caregivers or other children, they learn essential social skills such as sharing, taking turns, and cooperating, which are crucial for later social interactions.
Furthermore, screen-free play supports language development. When caregivers interact and talk with babies during play, they introduce new words, concepts, and language patterns, fostering communication skills.
Limiting screen time allows babies to focus on real-world experiences, enabling them to explore their surroundings, experiment with different materials, and learn through hands-on interactions. This active engagement with the physical world lays the foundation for their learning and understanding of the environment around them.